Project Management with a Bit of Magic
Plan, manage, and deliver projects efficiently. Merlin Project for macOS and iOS
Mind mapping lets you visually organize thoughts, solve problems, and boost creativity. In this guide, you'll explore the science behind mind mapping, step-by-step techniques to create your own, and expert tips to refine your approach. Ready to map out your next big idea? Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
Introduction to Mind mapping
The Science Behind Mind Mapping
How to Create a Mind Map: Step-by-Step Guide
Tips & Tricks
Use Cases of Mind Maps
The right Toolkit for Mind Mapping
Creative Project Management with Merlin Project
Final Thoughts
FAQs
Mind maps are more than just doodles on paper. They help you organize your thoughts, structure information, and dissect problems visually. Whether you’re brainstorming ideas, planning a project, or learning new concepts, mind mapping engages both logic and creativity — boosting comprehension, recall, and collaboration along the way.
Mind mapping offers tangible benefits to anyone seeking clarity and structure. For instance, a 2020 study has revealed that "visual communication" can improve memorization. During the study, participants' test results improved by ~30% due to visual communication.
A mind map is like a shortcut for your brain. It grants faster access to ideas, simpler connections, and fewer mental roadblocks. Moreover, mind maps free you to explore creative angles that might be missed in linear note-taking. If you’re looking to maximize creativity and enhance problem-solving skills, mind mapping is a strategy worth your time.
A mind map is a visual representation of information that starts with a central theme and branches out into related topics. It mirrors the way your brain naturally forms connections, using colors, keywords, and imagery to spark new ideas.
Tony Buzan, an English author and educational consultant, popularized mind mapping in the 1970s. He believed that traditional note-taking was restrictive and failed to capitalize on the brain’s full creative potential. Legend has it that while Tony was revising for exams, he noticed that highlighting keywords and using colorful images helped him remember concepts more effectively. As he taught others these techniques, he coined the term “mind map” to capture the essence of branching, radiant thinking. Over time, he refined this approach—combining art, psychology, and memory training to create a method accessible to anyone. Learn more on Tony Buzan’s ideas.

The human brain does not process information in a linear fashion. It thrives on relationships, patterns, and connections.
Tony Buzan
Mind mapping isn’t magic; it’s science-based. It capitalizes on how our brains are wired to process and store information. By merging visual cues with logical structures, mind maps activate multiple mental pathways, increasing both comprehension and recall.
A widely cited statistic claims that the human brain processes visuals 60,000 times faster than text. However, since its first mention in 1997, no scientific evidence has supported this claim. In fact, there’s even a $60 reward for anyone who finds the original source. Regardless of this questionable number, one thing remains true: Visual data helps us remember information better.
Psychologists such as Dr. John Medina emphasize that our memory centers — including the hippocampus and frontal cortex — form stronger neural connections when exposed to colorful and distinct visual stimuli. This visual engagement sets the stage for deeper comprehension and more robust memory. In essence, the more senses you involve and the more unique the stimulus (color, shape, imagery), the more “hooks” your brain creates to retrieve that information later. (Picture Superiority Effect)
By understanding how memory forms in these brain regions, you can strategically boost both retention and comprehension. Techniques like chunking (grouping related ideas) or using associative images build a mental landscape that’s easier to navigate. As you’ll see in the next section, mind maps seamlessly harness visualization to amplify learning outcomes.
Mind mapping’s effectiveness is grounded in core psychological and cognitive principles:
Association techniques (Linking concepts creates meaningful connections)
When you draw a line between two ideas, you forge a mental link. Each node and branch reflects how concepts overlap or diverge. For instance, connecting a “marketing” branch to a “customer behavior” branch makes it easier to see cross-functional insights. This constant linking process helps your mind store and retrieve information in a more dynamic way than isolated note-taking.
Memory via visualization (Colorful layouts and imagery improve recall)
Picture a bright red branch labeled “Urgent Tasks” and a blue branch labeled “Long-Term Goals.” Your brain immediately categorizes these ideas based on color, forming a visually memorable structure. Psychologists have long noted that dual-coding — combining visual elements with text — cements memories more effectively than text alone.
Creativity (Unstructured brainstorming promotes out-of-the-box thinking)
Because mind maps don’t force you into a rigid, linear path, you’re free to leap to unexpected associations. Rather than following a prescribed sequence, you explore parallel tracks of thought. This freedom often sparks innovative concepts that might never emerge in a simple list or outline.
Collaboration (Shared mind maps foster teamwork and alignment)
On a team level, visual brainstorming sessions break down communication barriers. A shared mind map helps each member see how their ideas fit within the bigger picture. By centralizing notes and sketches in one place, the team can align on goals, responsibilities, and timelines, making group work more coherent and collaborative.

Tell me and I forget, teach me and I may remember, involve me and I learn.
Benjamin Franklin
Follow these actionable steps to start mapping your ideas effectively:
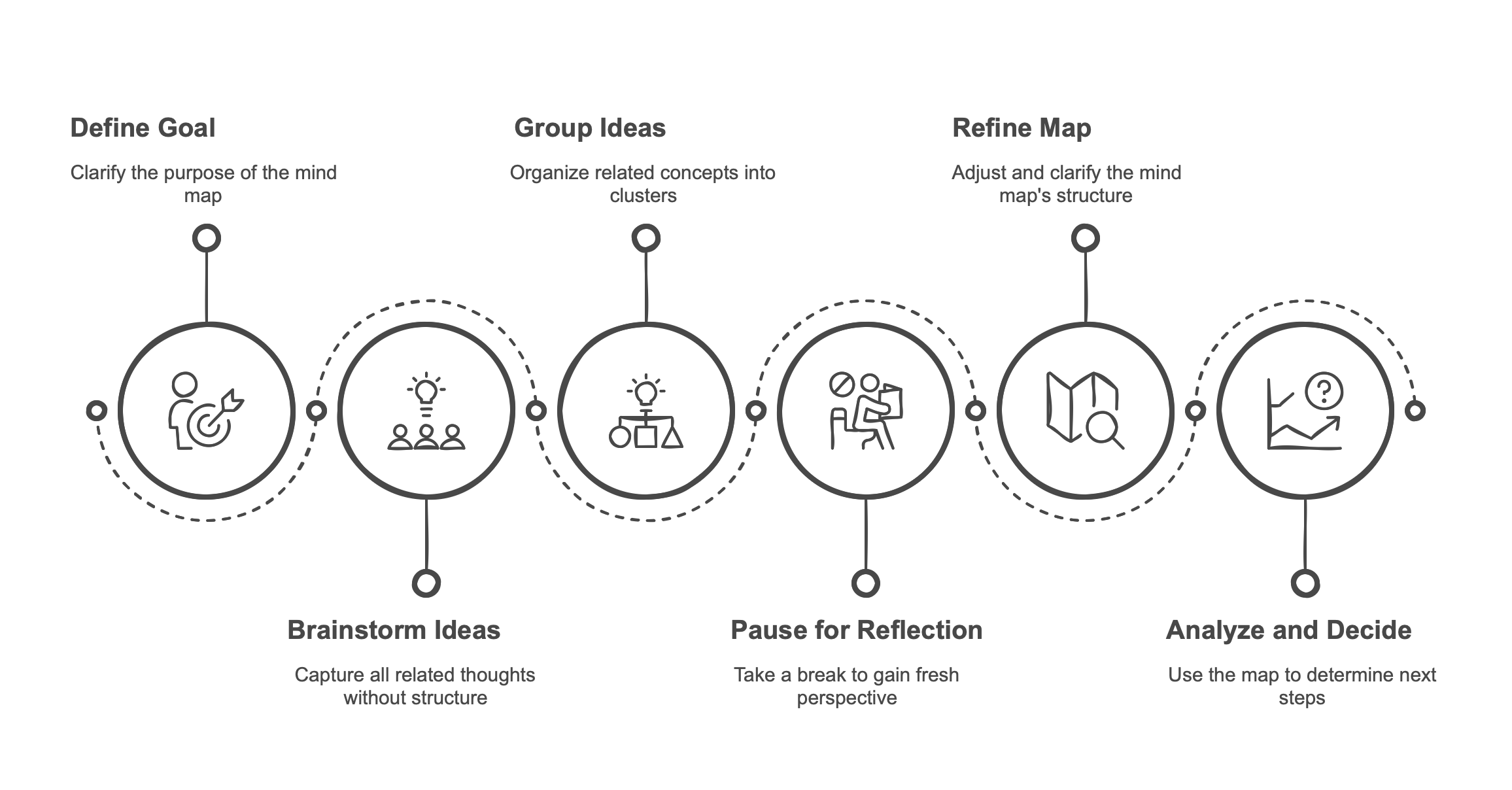
Define your goal:
Begin by clarifying why you’re creating the mind map. Are you planning a project, solving a problem, or studying a new subject? Clearly identifying your objective keeps your focus sharp. Set a tangible outcome for the session, such as generating a list of next steps or organizing a specific set of data. With a well-defined goal, you’ll be better equipped to filter out irrelevant information and keep your map streamlined.
Start brainstorming:
Jot down all ideas that come to mind related to your central theme. Don’t worry about structure or hierarchy just yet. Capture all thoughts, words, images, or phrases that pop up. If you’re working in a group, use sticky notes or a digital tool so everyone can contribute simultaneously. Embrace this free-flow stage to unlock creative thinking without constraints.
Group ideas:
Once you have a pool of ideas, begin to cluster related concepts together. If certain topics naturally belong together — like “budget,” “resources,” and “timeline” — place them in the same branch. This grouping reveals emerging patterns or themes. Think of it like organizing a messy desk: grouping similar items not only tidies up the space but also helps you locate what you need faster.
Pause for reflection:
Step away from your mind map for a short break. Fresh eyes often spot gaps or inconsistencies. Coming back later, you might notice that one cluster could use sub-branches, or that another branch is superfluous. This pause ensures that you don’t settle for a half-baked structure.
Refine and revise:
After your break, refine your mind map by adding or removing branches, clarifying labels, and reorganizing connections. Aim for clarity: remove duplicates, fix typos, and adjust the visual layout so it’s easy on the eyes. This step transforms your initial brainstorm into a structured visual map that communicates its purpose and content.
Analyze and decide:
Finally, use the mind map to drive decisions or next steps. Identify patterns, prioritize tasks, or plan your follow-up actions. A mind map is only as useful as the insights it generates. Translate those insights into steps you can act on right away. By this point, you have a powerful tool to guide strategy, solve problems, or keep your team aligned.
Think of your mind map as a tree. The central theme is the trunk, while branches and sub-branches are your main ideas and supporting details. Start with broad categories and narrow your focus as you branch out. This hierarchical approach helps maintain clarity and ensures you don’t miss key points.
Colors make your map engaging and help segregate ideas. Assign a specific color for each main branch and stick to it. Plus, use colors for prioritizations, e.g. red for urgent tasks, etc. Likewise, create a visual hierarchy: major ideas in bigger, bolder fonts; sub-ideas in smaller type. Consistent formatting and color schemes speed up comprehension and reduce visual clutter.
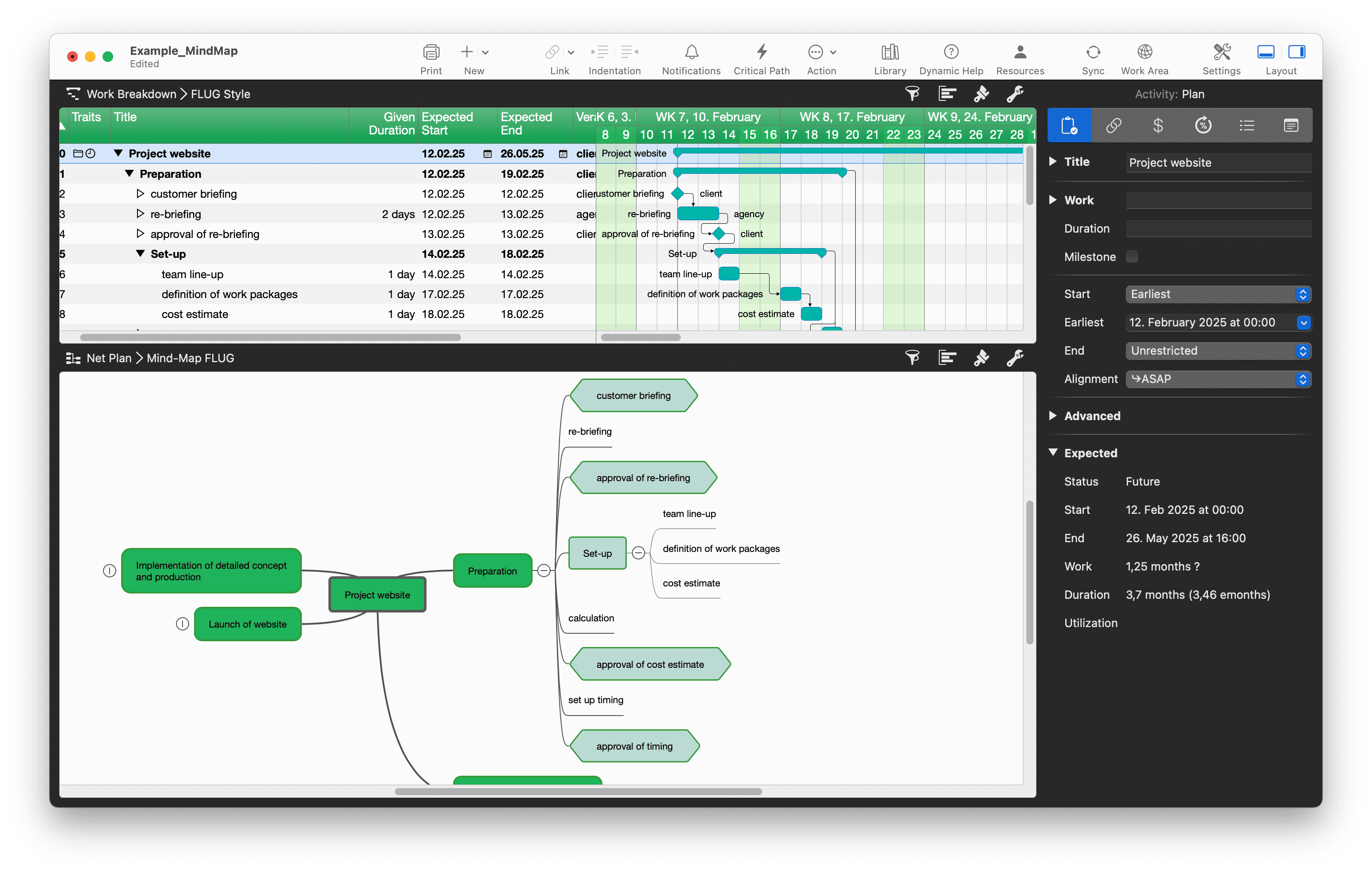
Use the mind map view as an alternative way to display the project plan. The mind map is just another view type of the Merlin Project file. The details section also allows you to view and edit two view types parallel. This is helpful when it comes to fine-tuning the project.

When a new project type that is not an everyday occurrence is started, work packages are often collected in the team during the kick-off and then gradually worked out in detail. I like to use the mind map view in the kick-off, where I capture all the work packages, milestones and even first detailed steps. With a single click, I can then switch to the work breakdown view and have a fantastic basis for my project plan. Setting this up is then quick and easy - as if by magic.
Kathrin Lamm, Certified Trainer for Merlin Project
Short, punchy keywords trump lengthy sentences in a mind map. They’re quicker to read and easier to remember. Maintain parallel structure (e.g., “Plan,” “Execute,” “Review”) to ensure a coherent flow. Icons can also enhance recognition. Use simple symbols (like a calendar for deadlines or a lightbulb for creative ideas) to give immediate context.
If you find certain nodes are rich with data (such as budget numbers, references, or attachments) consider layering that information behind hyperlinks or pop-up notes if your tool allows it. This way, you keep the primary view clean while still having quick access to more details.
When multiple people contribute to one mind map, confusion can arise if changes happen simultaneously. Use a digital tool with version control or real-time editing features. This ensures you track modifications, avoid overwriting each other’s work, and always have a backup of earlier versions if you need to revert changes.
Mind maps excel at nurturing fresh ideas. By visualizing thoughts in a non-linear format, you create mental space for creativity to bloom. Common brainstorming techniques that mesh well with mind mapping include:
Mind maps break down complex issues into digestible parts, making it simpler to tackle root causes and propose solutions. One effective framework is the MECE principle: Mutually Exclusive, Collectively Exhaustive. Popular in management consulting, MECE ensures every category is distinct (no overlap) and collectively covers every possibility (no gaps).
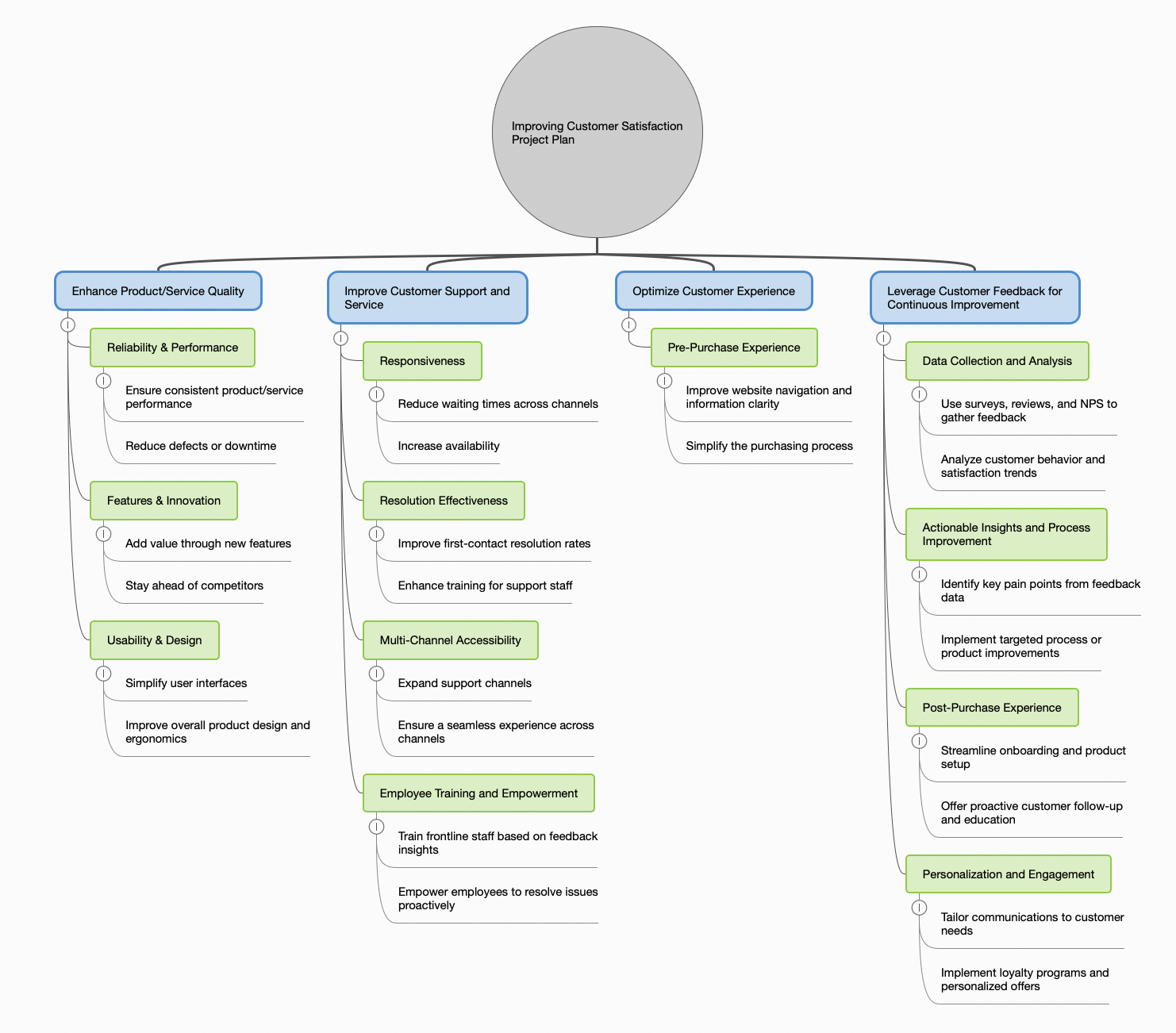
Identify the Core Problem
Place the main issue or question at the center (e.g., “Improving Customer Satisfaction”).
Create Top-Level MECE Branches
Branch out to primary categories ensuring they’re mutually exclusive — like “Product-Related Issues,” “Service-Related Issues,” and “Pricing-Related Issues”. These categories shouldn’t overlap. Also, these categories should be collectively-exhaustive as they capture the problem statement from all possible angles.
Expand Each Branch Exhaustively
Under each branch, list sub-factors so that, collectively, they address every angle. For “Service-Related Issues,” you might have “Communication,” “Response Time,” and “Quality of Support” as sub-branches.
Analyze and Prioritize
Once the tree is complete, analyze which categories or sub-branches hold the highest impact. A visual highlight or color-coded rating can help you see which areas need immediate action.
Formulate Action Steps
Finally, convert each sub-branch into a clear to-do list or solution path. Because the structure is inherently logical and comprehensive, you’ll have a robust, gap-free strategy.
Mind mapping can be done with pen and paper or via digital tools. Paper offers freedom to sketch anywhere, anytime—perfect for quick personal notes or creative doodling. But it’s less convenient for large projects, collaboration, or frequent updates. Digital software, on the other hand, offers powerful features like real-time editing, easy reorganization, and multimedia integration—ideal for team-based, dynamic work.
When choosing a digital tool, look for features that enhance your creative process and meet practical needs, from brainstorming with AI to exporting professional reports:
Modern mind mapping applications, such as Merlin Project, harness artificial intelligence (AI) to support brainstorming. AI can cluster similar ideas automatically, suggest potential connections you might overlook, and even generate starter mind maps based on a prompt. This is a game-changer if you’re tackling a broad topic and need an extra boost to kickstart creativity or organize a mountain of ideas.
In today's connected work environment, collaboration is essential. Choose software with automatic synchronization so that all team members can work from anywhere. Real-time collaboration features ensure that changes are instantly visible, enable direct communication within the tool, and ensure that everyone is working with the same up-to-date information.
Sometimes you need more than just a mind map; you need a polished presentation for stakeholders or clients. Tools with reporting features — filtering, hierarchy views, and multiple export options — help you tailor the final view for your audience.
Mind Mapping for Ideation
Merlin Project elevates brainstorming by seamlessly integrating intuitive mind mapping with robust project planning. Begin by capturing and organizing your ideas in a free-flowing mind map, where you can quickly add nodes, branch out concepts, and visually structure your project’s core themes—all within a single, user-friendly interface.
From Creativity to Detailed Planning
When you're ready to transition from creative ideation to detailed planning, Merlin Project lets you convert your mind map into a comprehensive work breakdown structure. This transformation automatically organizes your ideas into structured tasks, complete with start and end dates, dependencies, and resource assignments. Whether you prefer traditional Gantt charts or agile Kanban boards, every view remains synchronized so your project data is always current.
Unified Views & Real-Time Collaboration
By unifying the creative process with rigorous project management, Merlin Project provides the flexibility to iterate your ideas while maintaining a single source of truth across all planning views. This real-time synchronization enhances team collaboration, empowers you to adapt quickly to changes, and ultimately streamlines your workflow from initial brainstorming to final execution.
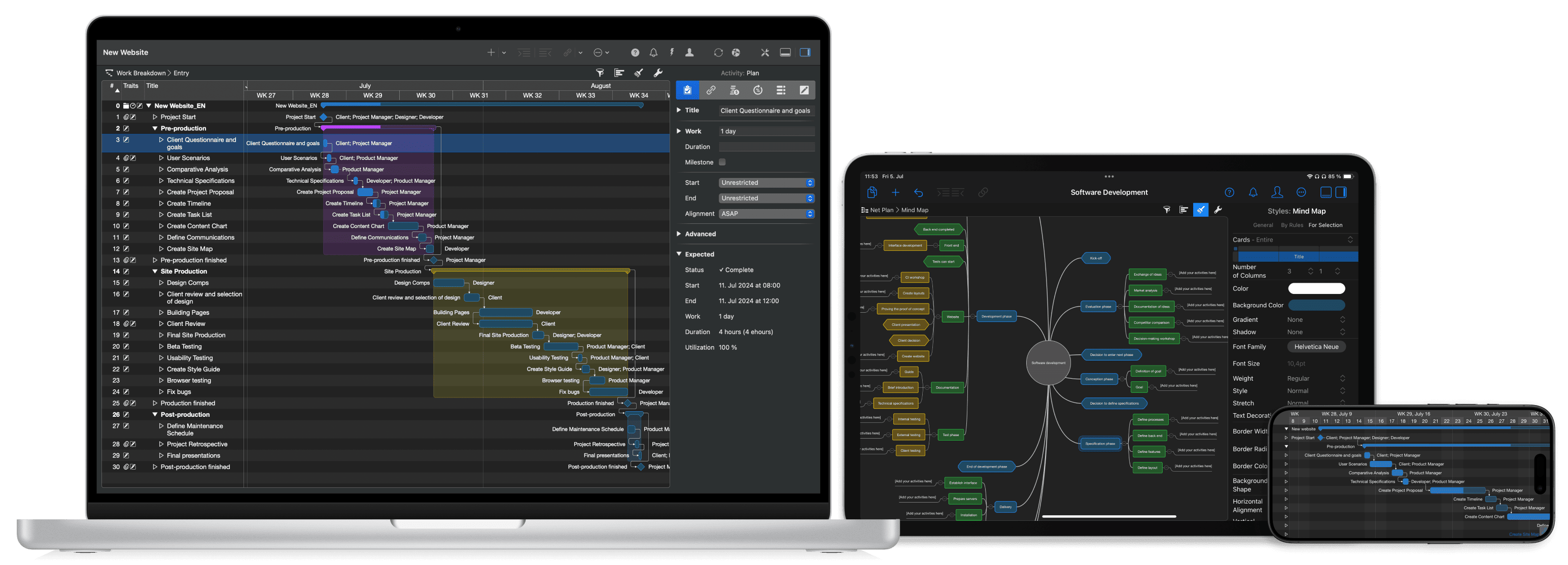
Plus, you can get really creative with our Mind Maps. Here are two examples:
Mind mapping is a game-changer for anyone seeking a structured yet creative approach to tackling problems, organizing information, or collaborating effectively. Whether you prefer the tactile feel of pen on paper or the expansive capabilities of digital tools like Merlin Project, the core principles remain the same: visualize, connect, and refine.

If you can visualize it, if you can dream it, there's some way to do it.
Walt Disney
Ready to take your first step? Dive into the resources linked throughout this guide or open a fresh canvas and start mapping out your next big idea. Your brain—and your projects—will thank you!
Your ideas, our magic – make projects easy! Test now 30 days for free.
