Project Management with a Bit of Magic
Plan, manage, and deliver projects efficiently. Merlin Project for macOS and iOS
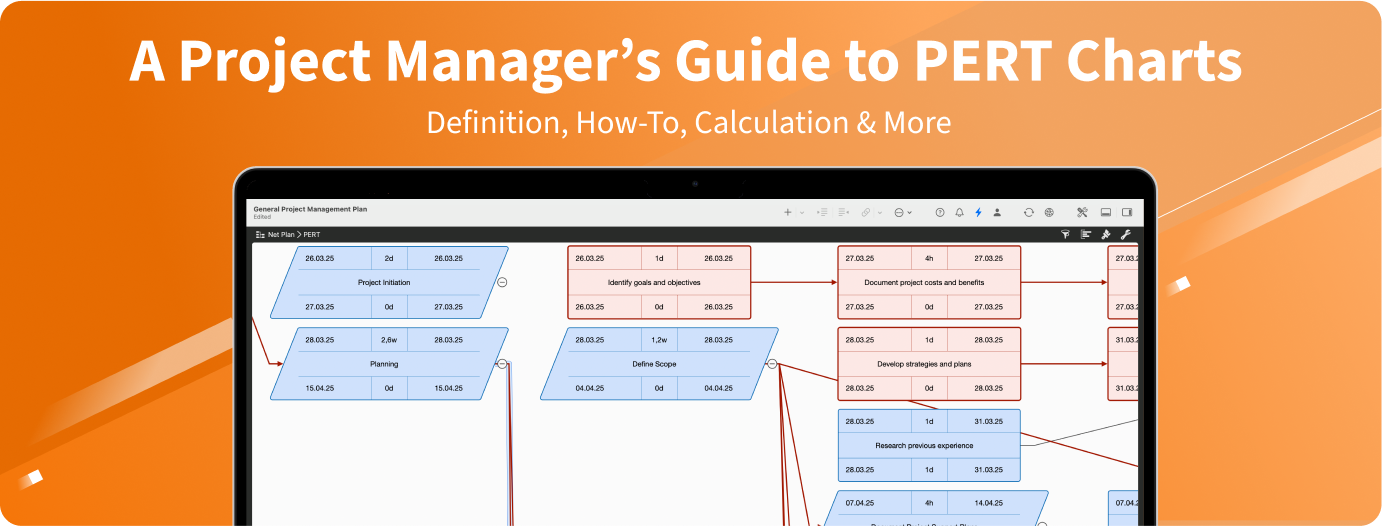
PERT charts are a basic project management tool to organize, schedule and coordinate project activities. Learn the advantages and disadvantages of this method.
Table of Contents
What Is a PERT Chart?
Advantages and Disadvantages of a PERT Chart
The Core PERT Methodology: Time Calculation
How to Create a PERT Chart Step-by-Step
When to Use a PERT Chart vs. Other Tools
Example: Calculating a Task’s Duration with PERT
Practical Tips
Conclusion
A PERT chart (Program Evaluation and Review Technique) is a project management tool designed to visualize the activities in a project, their logical dependencies, and their chronological sequence. It goes beyond the work breakdown structure (WBS) by highlighting not only relationships among tasks but also the sequence in which they should be carried out. This helps project managers identify the critical path (i.e., the sequence of tasks that directly affects the total project duration) and any time buffers (slack).
Tip: Explore the Merlin Project Learning Path for more Project Management Tips & Tricks
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| The preparation makes it necessary to think through the entire project and not just individual sub-areas. In this way, open points become visible. | The creation is relatively complex. |
| The network plan creates a meaningful overview of all project activities and their mutual dependencies. | The presentation requires training in order to fully capture the information content. |
| The plan can be easily updated. | The more detailed the network, the higher the control effort to avoid planning errors. |
| A relatively exact scheduling and thus cost saving is possible. | The method is oversized for small projects. |
| Bottlenecks (critical path and buffer) are easy to recognize. | |
| The network can be developed independently of schedule assumptions. | |
| The plan is a clear communication tool for the project managers. |
Tip: Net plan technology (including PERT charts) is most beneficial for larger or complex projects. For simpler or shorter efforts, you may find agile PM methods with Kanban boards or Gantt charts more intuitive and less time-consuming to set up.
A defining feature of the PERT method is its approach to time estimation for tasks. Instead of a single guess, PERT uses three estimates to capture uncertainty:
Using these three estimates, PERT calculates an expected duration (TE) for each activity, typically using the formula:
TE = (O + 4M + P) / 6
You can also calculate the variance or standard deviation for each task to assess the probability of finishing on time, although many modern project management applications (like Merlin Project) handle these calculations automatically.
Even though many project management tools automate most steps, it’s essential to understand the underlying process:
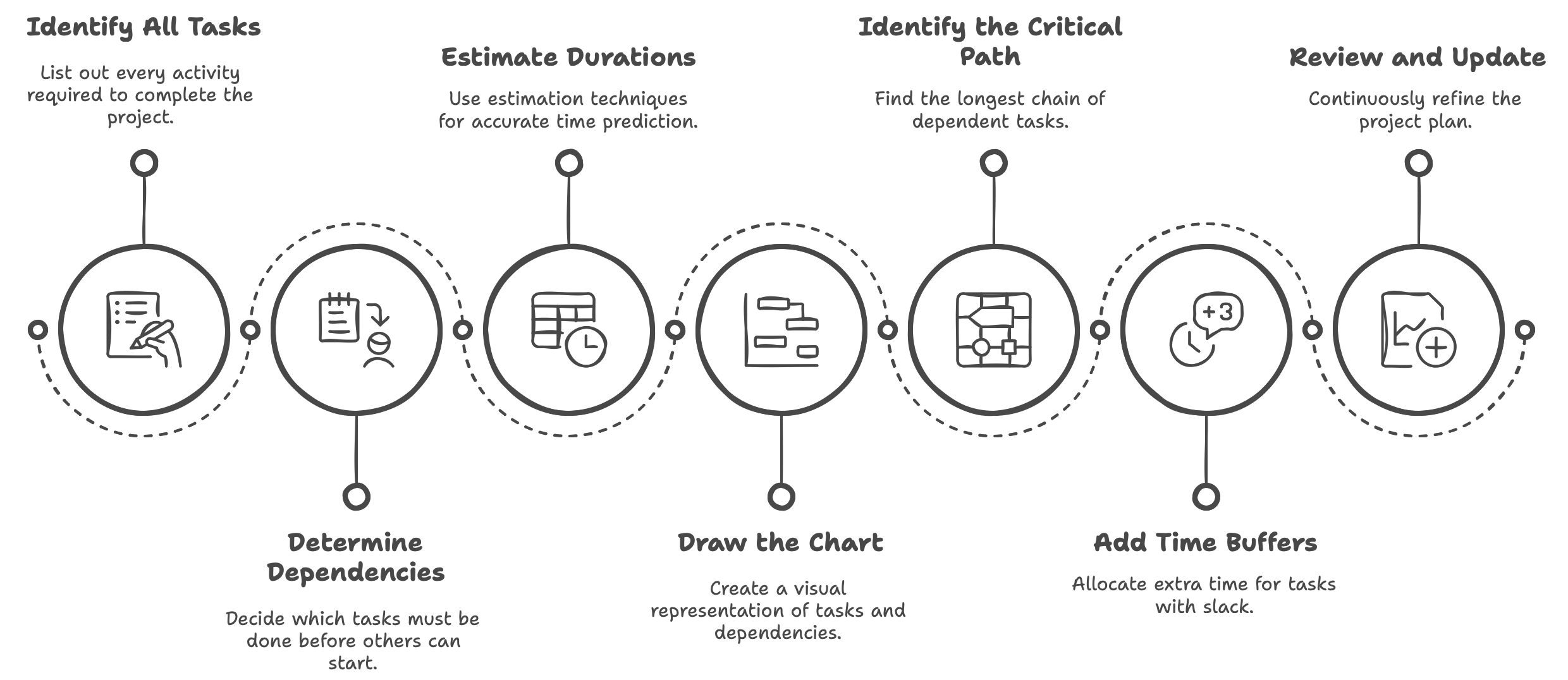
Identify All Tasks
Determine Dependencies
Estimate Durations
Draw the Chart
Identify the Critical Path
Add Time Buffers
Review and Update
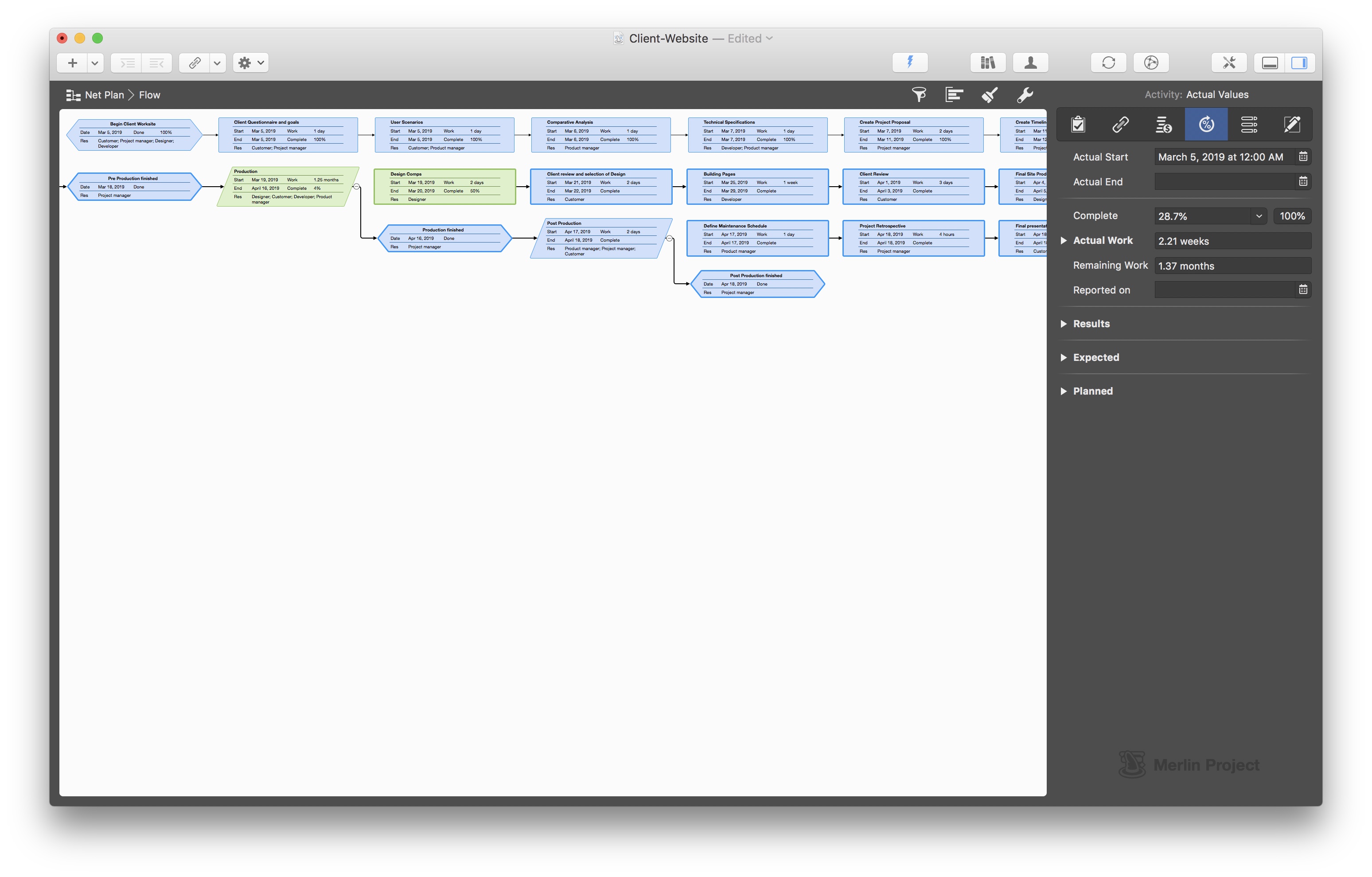
Modern project management involves numerous methodologies and tools, each serving different project types and sizes:
Key Consideration: PERT can be adapted into hybrid frameworks. Some teams use a PERT chart for overall scheduling and Kanban or scrum boards for daily task management.
Imagine you have a task: Develop Prototype
Using the PERT formula:
TE = (O + 4M + P) / 6TE = (5 + 4*8 + 14) / 6TE = (5 + 32 + 14) / 6 = 51 / 6 ≈ 8,5 days
Thus, you’d plan around 8.5 days for the task. Many project management tools allow you to enter three time estimates and perform these calculations automatically.
A PERT chart is far more than a static diagram—it’s a strategic planning tool that helps you conceptualize complex projects, pinpoint the critical path, and incorporate uncertainty into time estimates. While it can require more effort to set up compared to simpler methods like Gantt Charts or Kanban boards, it excels in bringing clarity to large-scale, multifaceted projects.
With modern software automating the calculations, learning curve, and chart updates, incorporating PERT into your workflow can elevate your project management capabilities.
Your ideas, our magic – make projects easy! Test now 30 days for free.
