macOS Hints: Improving WiFi Reception On Mac For Your Home Office

What to do if surfing on Wi-Fi doesn’t work optimally? On a Mac, the operating system has hidden options for checking Wi-Fi quality.
Checking the Quality of Wi-Fi Reception on a Mac
Hold down the Option (alt) key on the keyboard and simultaneously click on the Wi-Fi icon at the top right of the menu bar. This will reveal additional options in the drop-down menu. They show various details about the Wi-Fi network your Mac is connected to.
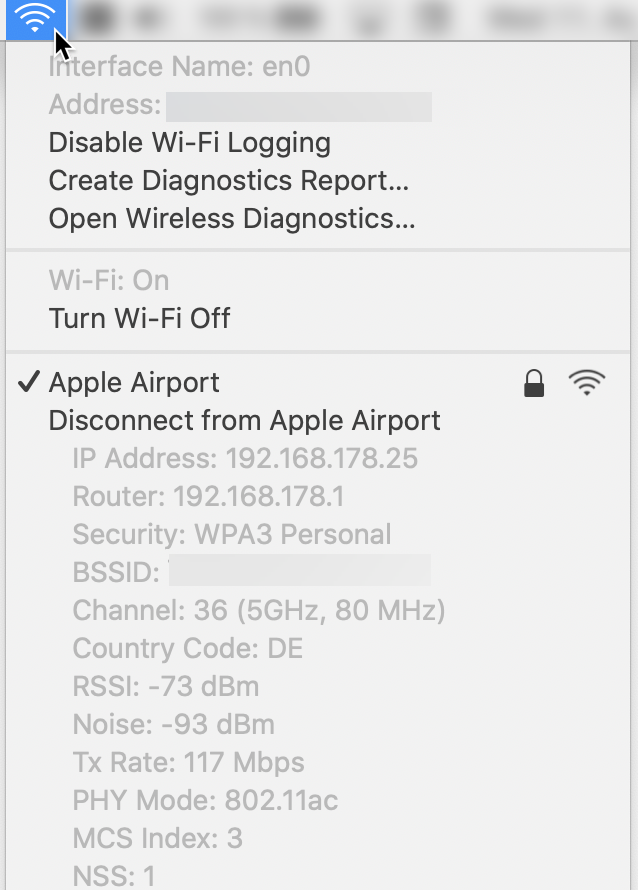
Among other things, you’ll find:
- Your Mac’s IP address
- The Wi-Fi router’s IP address
- The security of the Wi-Fi router (e.g. WPA3)
- Wi-Fi channel and associated radio frequency (2.4GHz or 5GHz)
- RSSI
- Noise (interference signal)
- Tx-Rate (speed in Mbit/s)
- PHY mode, i.e. the Wi-Fi standard (e.g. 802.11n)
Improving Wi-Fi Reception
For very good reception, the RSSI value should be better than -60 dBm; for example, if it’s around -75 dBm, reception is worse. Various factors can weaken a Wi-Fi connection:
- Objects located between the Wi-Fi router and your Mac (especially massive concrete walls, steel and metal structures, aquariums, and flat-screen TVs).
- Other devices that either use or interfere with Wi-Fi (mobile phones, iPads, microwaves, etc., and particularly other routers in the vicinity).
If you have a poor RSSI value, try to eliminate the interference sources mentioned above. If many other Wi-Fi routers are nearby, the noise level will be higher. In this case, enabling an automatic channel selection in the router can help.
| Metric | Very Good | Good | Poor |
|---|---|---|---|
| RSSI (dBm) | better than -50 | -50 to -65 | worse than -70 |
| Noise | lower than -90 | -70 to -90 | higher than -70 |
| Tx-Rate | higher than 500 Mbit/s | 100 to 500 Mbit/s | lower than 100 Mbit/s |
Example:
- An RSSI value of -45 dBm is considered very good, while -75 dBm is already poor.
- A noise value of -95 dBm indicates virtually no interference (very good), whereas -60 dBm signals heavy interference (poor).
This makes it easy to assess the Wi-Fi reception quality in your workspace and whether further steps are necessary.
Also try different spots in your home office to find where your Mac gets the best reception. Keep an eye on the RSSI value (the higher than e.g. -40 dBm, the better) and aim for low noise (around -100 is ideal!).
If you’re still having major issues, Wi-Fi repeaters (in a mesh system) can help, or you can use LAN cables (Ethernet) for data transfer.
That way, you’ll definitely be able to surf the internet in your home office without issues and finally focus on working with Merlin Project.
In Detail: What Do These Metrics Mean?
RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator):
This metric indicates the signal strength of the Wi-Fi network your Mac is connected to, measured in decibel milliwatts (dBm). The closer to 0, the better the signal quality. Values between -50 dBm and -65 dBm are considered good; below that, quality decreases significantly.
Noise (Interference Signal):
Indicates the strength of interference sources (other Wi-Fi networks or electrical devices) in the environment. A lower value (e.g. -95 dBm) means fewer disruptions and thus better Wi-Fi quality. Values around -60 dBm suggest many disruptions, reducing your connection quality.
Tx-Rate (Transmit Rate):
Describes the maximum possible transmission speed between your Mac and the Wi-Fi router, measured in megabits per second (Mbit/s). The higher the number, the better your potential connection performance. However, actual speeds may be lower, as they’re influenced by factors like distance and interference.

