Essential Psychological Theories for Effective Project Management

Project management is a team discipline. Therefore, motivating the team is essential. Psychological models help achieve that goal. Here you will find an overview of the key models.
Overview of the Models
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
Herzberg's Two-Factor Theory
McClelland's Three Needs Theory
McGregor's X-Y Theory
Expectancy Theory
Creating a successful project goes beyond scheduling tasks and hitting deadlines; it's about inspiring and empowering people. For project managers, understanding the psychology behind motivation can make the difference between a disengaged team and a group that’s fully committed and productive. This is where psychological theories play a crucial role, offering practical tools to help motivate and manage teams effectively. Let's dive into five key theories that every project manager should understand to foster a more efficient, satisfied, and high-performing team.
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
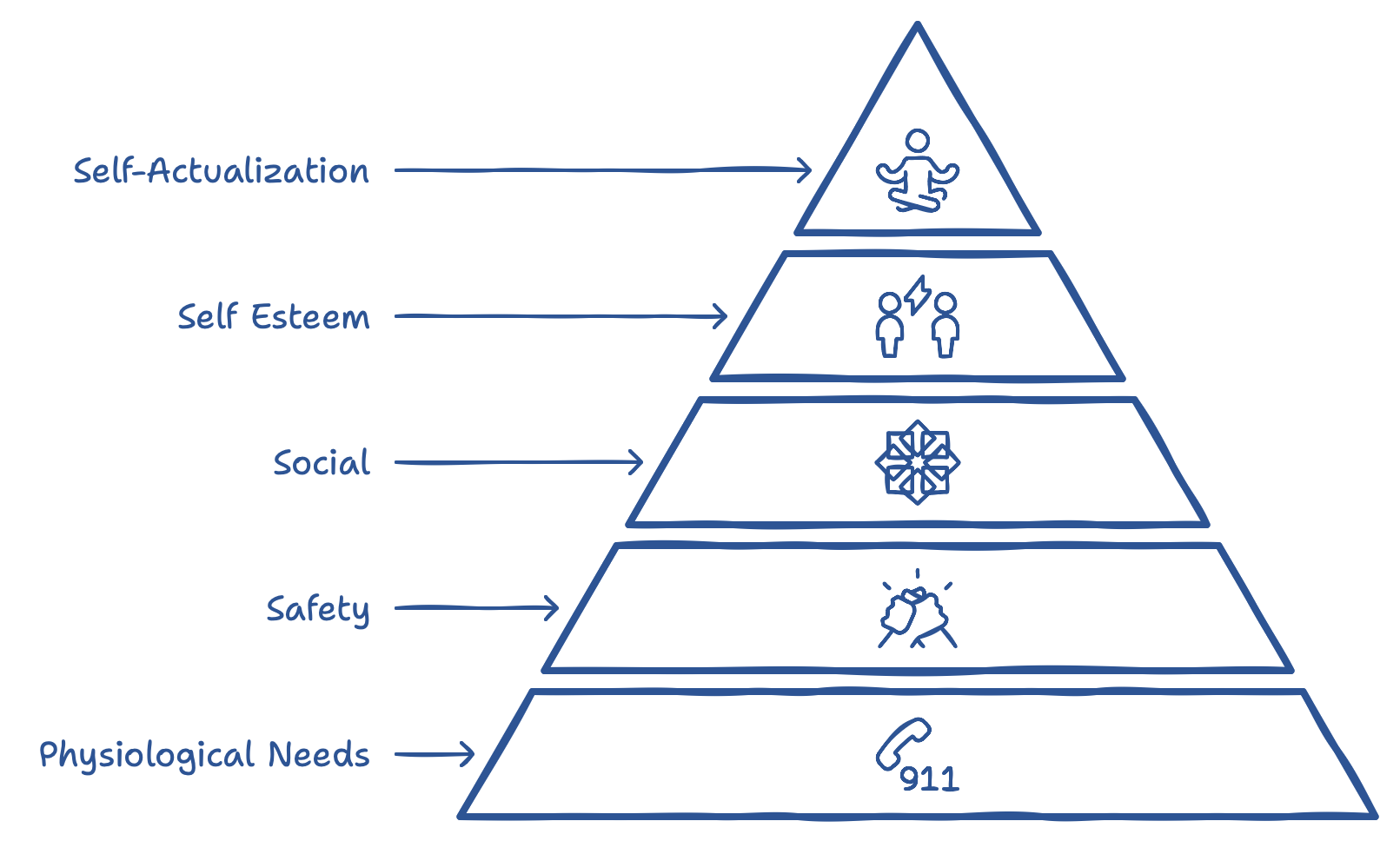
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs proposes that people are motivated by a sequence of needs, ranging from the most basic—like food and safety—to the more complex, such as self-actualization. In a work environment, this means employees first need security, structure, and trust in their role before they can focus on higher-level goals, like personal growth and team collaboration. As a project manager, you should prioritize a safe, well-organized work environment where team members feel respected and heard. By addressing these basic needs, you lay the groundwork for a culture where people are ready to pursue larger goals and stretch their potential.
Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory
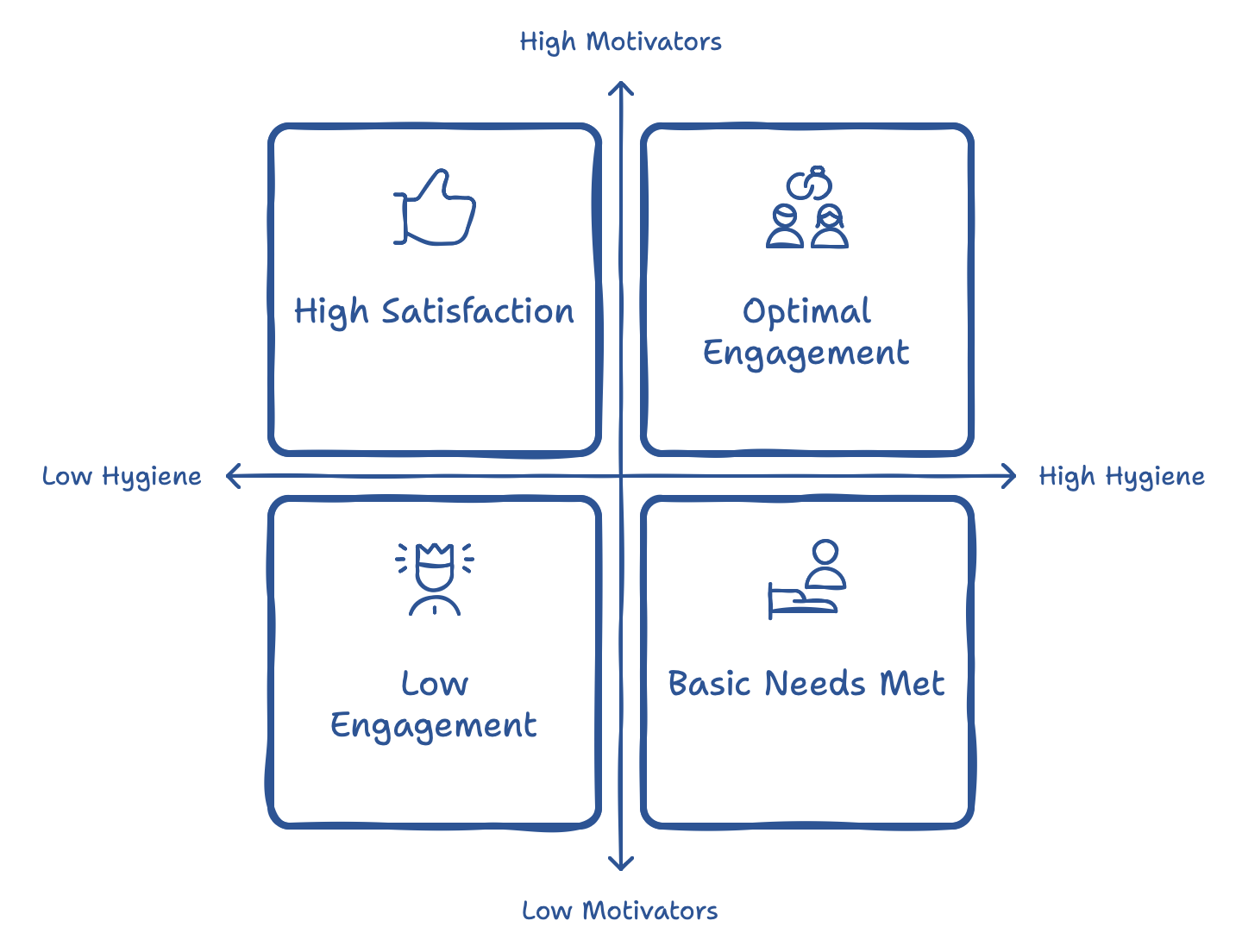
Herzberg’s Two-factor Theory divides workplace factors into "hygiene" factors, like pay and working conditions, and "motivators," such as recognition and meaningful work. Hygiene factors prevent dissatisfaction, while motivators actively increase satisfaction. If the basics—like a fair salary and a comfortable work environment—aren't met, dissatisfaction will arise regardless of other positive aspects. Once these basics are secure, adding motivators, such as acknowledging achievements or assigning challenging projects, can make work more enjoyable and rewarding. As a project manager, ensure hygiene factors are covered while also incorporating motivators to boost engagement and satisfaction.
McClelland’s Three Needs Theory
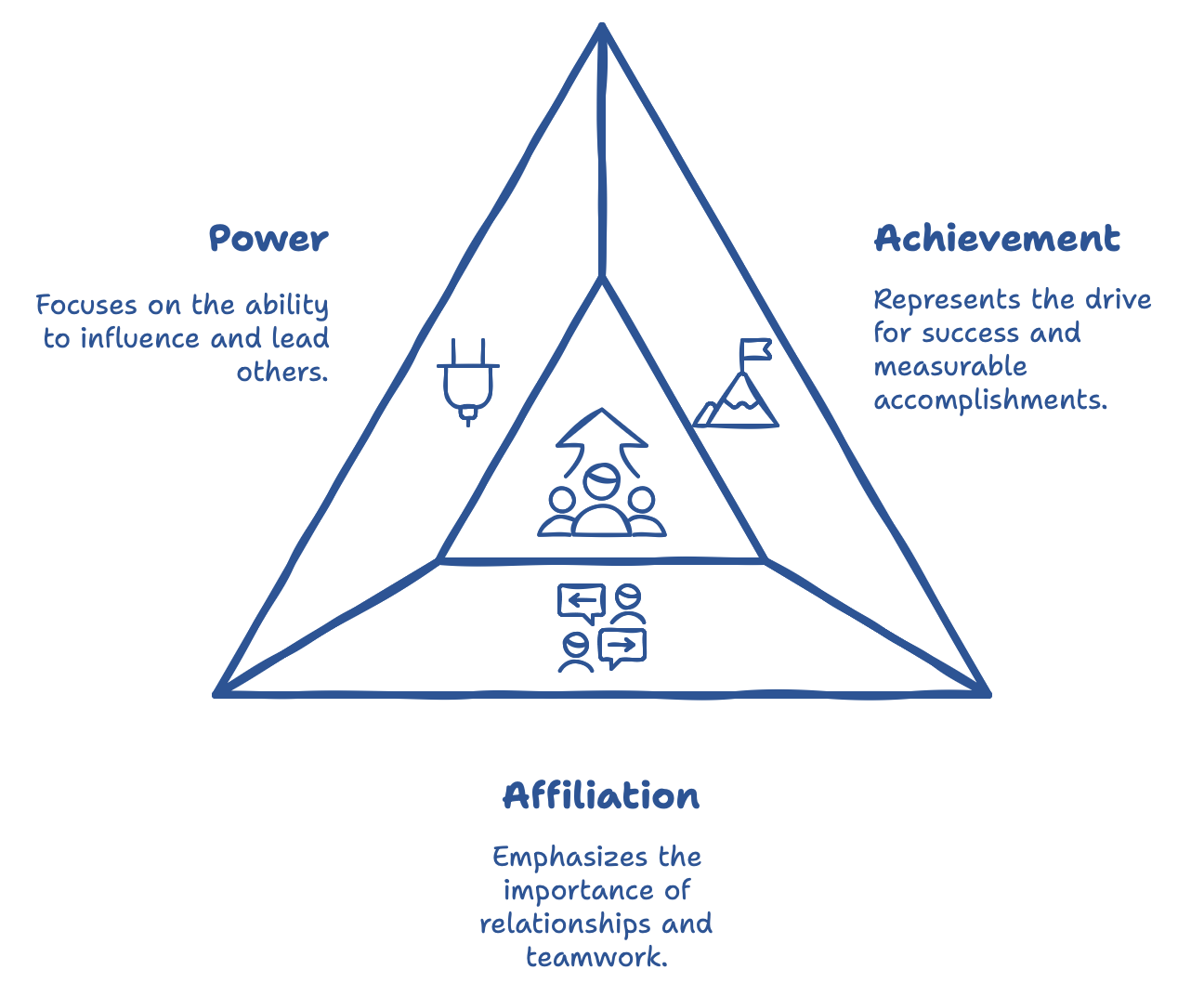
McClelland’s Three Needs Theory identifies three key drivers: achievement, affiliation, and power. Each individual has a unique mix of these needs, and understanding them can help you assign roles effectively. High-achievers, for example, thrive with challenging tasks that provide opportunities for measurable success, while those motivated by affiliation work best in collaborative settings where relationships are a focus. People driven by power, meanwhile, may excel in leadership roles where they can influence outcomes. By tuning into these individual drivers, you can assign tasks that best match each team member’s strengths, creating a balanced and dynamic team.
McGregor’s Theory X and Theory Y
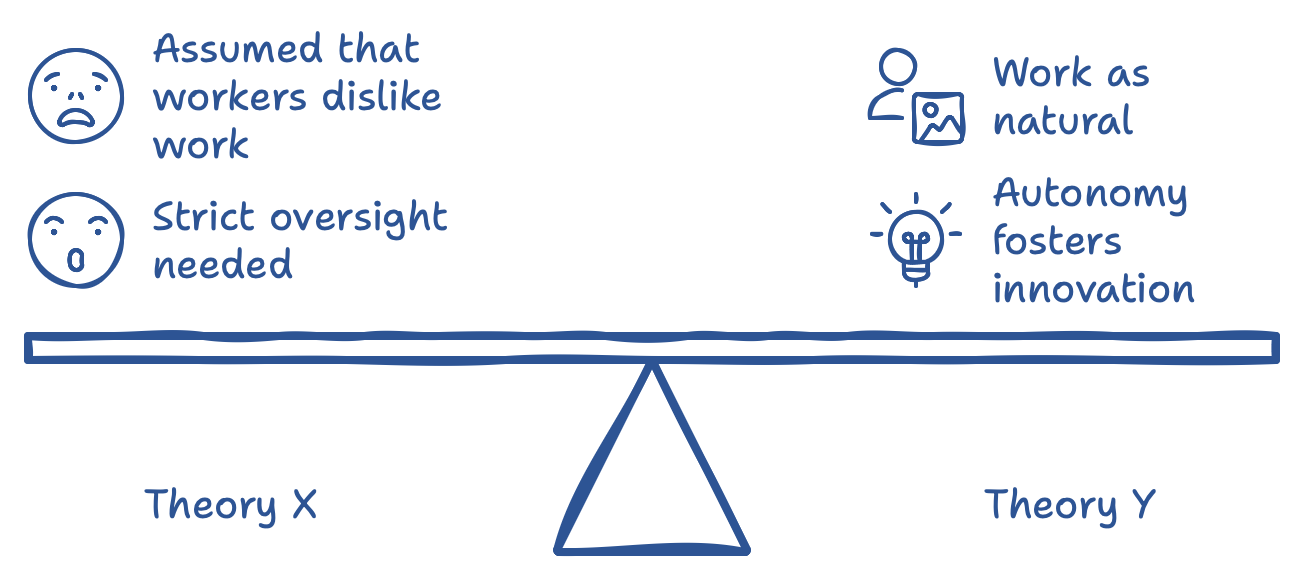
Douglas McGregor’s Theory X and Theory Y contrast two views of worker motivation. Theory X assumes people dislike work and need strict oversight, while Theory Y views work as natural, with people finding satisfaction in their roles when given responsibility and autonomy. Adopting a Theory Y approach empowers team members to take ownership of their tasks. Instead of micromanaging, you foster an environment of trust and autonomy, allowing the team to use their creativity to solve problems. When team members feel trusted, they’re more likely to innovate and stay motivated, knowing their contributions are valued.
Expectancy Theory
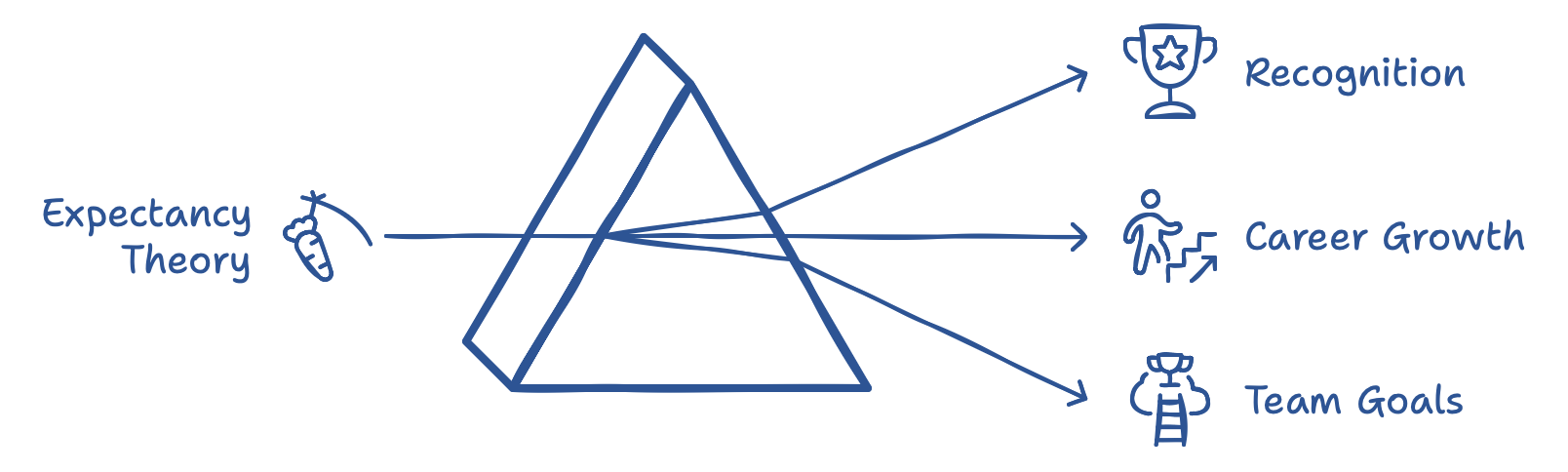
Expectancy Theory suggests that people are motivated when they expect their efforts to lead to desirable outcomes. If team members believe their work will yield meaningful rewards—whether that’s recognition, career growth, or achieving team goals—they’ll be more driven to perform well. To apply this, ensure that each individual understands how their specific tasks contribute to the overall project and make sure they’re aware of potential rewards or recognition. When people see a clear link between their efforts and positive outcomes, they’re motivated to stay focused, even during challenging phases.
Applying Psychological Theories in Real Life
Imagine you’re leading a cross-functional team on a high-stakes project with a tight deadline. Knowing the project’s success depends on strong team dynamics and motivation, you apply psychological insights to maximize productivity and engagement. Start with Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs: ensure every team member has clear guidelines, access to necessary resources, and a supportive environment. This basic security sets the foundation for high performance. Next, turn to Herzberg’s Hygiene Theory to address essential workplace factors. Providing good working conditions and ensuring fair treatment prevents dissatisfaction, while adding motivating elements—like public recognition for accomplishments and meaningful challenges—boosts morale and commitment.
To personalize motivation, McClelland’s Three Needs Theory is a valuable tool for assigning tasks. For instance, high-achievers excel with challenging, goal-oriented tasks, while those motivated by affiliation may shine in collaborative or team-based roles. By aligning tasks with these needs, you create a more effective team dynamic. With McGregor’s Theory Y, you can promote autonomy, inviting team members to take responsibility for certain areas of the project. Instead of micromanaging, trust your team to drive their tasks forward, which builds a sense of ownership and trust. Lastly, Expectancy Theory emphasizes aligning effort with rewards. Make sure each team member understands the link between their specific tasks and the project’s overall goals. When people see how their work directly contributes to success, along with a clear path to recognition or growth, motivation stays high, even in challenging phases. Applying these theories thoughtfully creates a positive work environment where team members feel valued, trusted, and driven to excel.
Boost Team Productivity with Merlin Project
Test Merlin Project 30 Days for Free. Hybrid Project Management on Mac, iPad and iPhone.
Understanding and applying these psychological principles can make a big difference in how you manage your team. But to truly optimize your project and stay on top of every detail, you need the right tool. Merlin Project can help you apply these insights more effectively, with powerful features that support task organization, resource management, and team collaboration. It’s designed to keep everyone aligned, reduce inefficiencies, and empower your team to achieve great results. Get started with Merlin Project today and experience a new level of project success!
If you have any questions about this blog article or would like to discuss it, we look forward to your contribution in our forum.

